Nowadays, one of the main causes of infertility is female aging.
Particularly in Spain, intending to become pregnant at a relatively late age is the top impediment for women to become biological mothers.
The delay in motherhood causes the laboratory of in vivo fertilization to age, affecting the quality and quantity of gametes (eggs) and the different organs and processes involved in reproduction.
In general, it is recommended to go to a fertility specialist if after a year of continuous and unprotected sex, pregnancy is not achieved in women up to 35-36 years of age. In the case of women over 36 years, we recommend going to a specialist after 6 months of trying. There are several causes of female sterility and it is common for women to have more than one at the same time.
What are the causes of female sterility?
- Genetic risk factors: Certain genetic syndromes or diseases, such as Fragile X Syndrome, can lead to an alteration in the ovarian reserve, making it difficult to get pregnant. In addition, many of the chromosomal abnormalities in the embryos are responsible for spontaneous and repeated miscarriages.
- Ovarian risk factors: Hormonal failures are due to a defect or an excess in the regulation of endocrine function such as polycystic ovary (PCOS), early menopause, ovarian failure and anovulation.
- Tubal risk factor: These are abnormalities found in the fallopian tubes that complicate the encounter of the egg with the sperm through the absence, impermeability, and obstruction of the tubes.
- Cervical risk factor: The anatomical and functional alterations of the cervix make it difficult for sperm to travel to the uterus and fallopian tubes due to previous surgery (conization) and the impermeability of the cervix (polyps and cysts).
- Uterine risk factor: It is more common for this type of alteration to cause infertility rather than sterility. They are characterized as alterations in the internal anatomy of the uterus – congenital or acquired – that can trigger repeated abortions.
Although these risk factors of infertility correspond to women, it is also convenient to talk about combined sterility, that is, when sterility affects both men and women. In these cases, the difficulty in conceiving is probably due to an immunological or also genetic cause.
Couples can be independently fertile but not be able to achieve pregnancy without assistance.
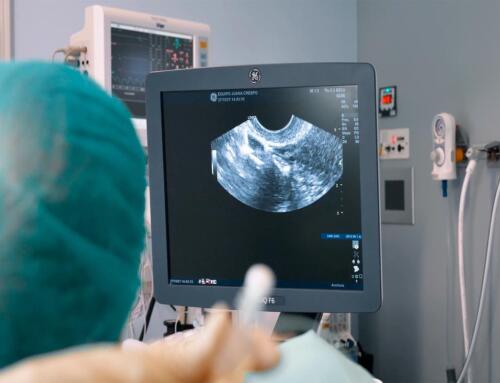
Main diagnostic tests to detect infertility in Equipo Juana Crespo
- Transvaginal ultrasound: This medical examination allows us to assess the number of visible follicles, the vascularization and the morphology of both the ovaries and the endometrium.
- Seminogram: This diagnosis requires the analysis and evaluation of stored semen after an abstinence of 2 or 3 days approximately.
- Hysterosalpingography: This consists of a radiological examination in which a contrast is injected into the uterus in order to determine the permeability of the fallopian tubes and other alterations in the uterus.
- Progesterone: This is performed in the mid-luteal phase, approximately on day 21 or 22 of the menstrual cycle.
- Basal hormone determinations: These are performed from day 2 to day 4 of the cycle: such as follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), also luteinizing hormone (LH), prolactin and estradiol.
In many cases our specialists also recommend other types of diagnostic tests on a case-by-case basis, for example:
- Karyotype: This is a test that is performed on the chromosomes.
- Sperm capacitation test: It is known as the “Mobile Sperm Count” (MSC).
- Hormonal and/or biochemical controls: This is a test that reflects the determination of prolactin, as well as thyroid hormones, insulin resistance and finally androgens.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Pelvis. It is a radiological test that can with or without contrast (depending on the patient’s previous history) that shows a detailed view of the woman’s entire uterus.
- Diagnostic Hysteroscopy: This test visualizes the uterine cavity and the fallopian tubes.
- Chlamydia Test: This test is used to determine if there is an infection that could have damaged the mucosa of the fallopian tubes.
- Diagnostic Laparoscopy: This is a very frequent diagnostic test that allows the woman’s reproductive organs to be easily visualized and thus evaluate the state of each one.
At Equipo Juana Crespo we prioritize the diagnosis of the possible causes of female and male sterility. Therefore, we prescribe all the necessary diagnostic tests in order to guarantee the maximum success of the assisted reproduction treatments. Feel free to contact us request and appointment on our toll-free number 800 041 82 2257 or through our form.